Internal Audit – the ISO 9001 Standard requirements for internal audits and program (part 2) – the audit program
The organization must maintain a documented program for conducting the audits. The program must be documented according to the ISO 9001 requirement. This is not a recommendation but a requirement! The purpose of this program is to ensure that the audits are conducted as planned. So, first, you need a program. The ISO 9001 Standard requires performing the audits within scheduled and fixed time frames. This requirement ensures that employees would know that the audit is a part of the quality management system and not a momentarily capricious decision made by the top management. It is recommended to publish the audit schedules. And for “surprise” audits – you need to define the time frames, just do not publish them.
The audits program must cover:
- Quality plans for the products – For any requirement for product realization, you must evaluate if it is performed as planned. The best way is to sample. Pick the product, review its quality plan, and check whether the product was realized according to the plan. Document the results.
- The ISO 9001 Standard requirements –Including the documentation requirements (customer complaints, purchasing information, CAPA, trainings, etc). The examination must be conducted throughout the entire organizational units which related to product realization or are under the quality management scope. Any unit must be examined at least once a year.
- Processes and procedures – the audit must evaluate whether the processes that are related to the product realization are performed as required. It could be a correlated with quality plans. But generally an audit must sample processes and evaluate its performance.
- Quality objectives – the audit must examine whether the organization is achieving his quality objectives. He evaluates the objectives – whether they are related to the product and evaluates the results. Where he revealed that the objectives are not fulfilled – he must be presented with reasons and measures.
It’s not easy being an auditor. It also not so easy to maintain all of the above without some help and guidance: Qualitymanualtemplates.com – The solution covers all the ISO 9001:2008 Standard requirements.
Internal Audit evident and findings
At the end of the audit the auditor must deliver a specific report about the audits evidences and findings. The report must specify:
- The auditee – the organization or unit that were audited.
- Who were the participants – it is recommended to document who participated during the audit. The purpose is clear. When the top management would like to conduct its inquiry – they would know where to start.
- General detail that shed light upon the auditee: how many workers, special projects, special recent events – information that would support the evidences. This is very important information.
- Reference to prior audits and prior findings – the auditor must verify that all nonconformities revealed during the last audit are eliminated, the treatment was documented and most important, they are not repeated.
- The audits findings according to the evidences – that mean what the auditor discovered and how is it referred to the criteria: good, requires an improvement action or requires a corrective action (we would not deal in this article with classification of findings). Actually this is the most important part of the report. It specifies what the auditor found. The auditor must document the evidences as accurate as possible.
- Recommendations – for every finding the audit may pay his recommendation.
- A sum of all nonconformities discovered during the audit – the purpose for the sum is:
- To gather all the nonconformities for the top management for a review
- To trace the corrective action for the next audit
This sum will become a corrective action report – but that is a whole different topic. Bear in mind – this report is designated for the top management and the function that is responsible for the auditee. That report is a tool for him to understand the status. Therefore it is recommended that the report would be in a format that is easy for him to understand. Look at the next diagram – we tried to visualize the process:
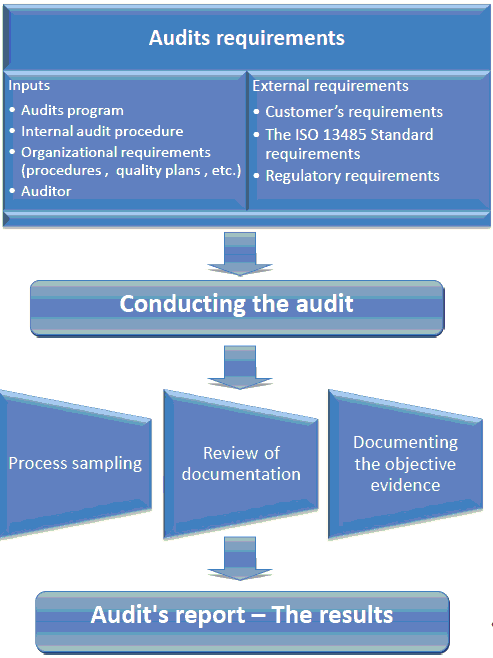
Off course it goes further but we will deal with that in another article. By the way, this diagram was made with Smart Draw software. Now, we know it could have looked better – but it makes the point and more important, it didn’t take us long and we sure don’t have any time to spare. We are busy people – like you. But sometimes it takes hours to document your quality management system, especially with the conventional tools (MS tools – including Visio), to draw the processes and to make the diagrams. On an average Quality management system you have dozens of diagrams. We know because we have been there. This software is really making our quality managers’ life much easier. Get your free trail now! SmartDraw.com.
Internal Audit summary
- The purpose of the audit is to ensure that the quality management system is as required by the ISO 9001 Standard and appropriately maintained.
- You are required to maintain a documented procedure specifying the process of the internal audit.
- The auditor bears a lot of responsibility. Therefore he must be perspective to the environment that he is auditing, must own the skills for evaluating and examining, with a wide view of matters.
- The auditor must be polite with high manners, and be patient and persistent. The audit is not an easy task to perform. The organization must maintain an audit program. The purpose of the program is to ensure that the audits are conducted as planned.
- At the end of the audit the auditor must deliver a specified report about the audit. This report is designated to the function that is responsible for the auditee.
